The vulnerability revealed this week by security researchers at Qualys, who dubbed it Ghost, could be taken advantage of through WordPress or other PHP applications to compromise web servers.
The glitch is a buffer overflow that can be triggered by an attacker to gain command execution privileges on a Linux machine. It is present in the glibc’s “__nss_hostname_digits_dots()” function that can be used by the “gethostbyname()” function.
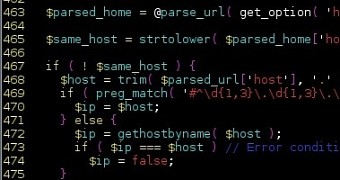
PHP applications can be used to exploit the glitch
Marc-Alexandre Montpas at Sucuri says that the problem is significant because these functions are used in plenty of software and server-level mechanism.
“An example of where this could be a big issue is within WordPress itself: it uses a function named wp_http_validate_url() to validate every pingback’s post URL,” which is carried out through the “gethostbyname()” function wrapper used by PHP applications, he writes in a blog post on Wednesday.
An attacker could use this method to introduce a malicious URL designed to trigger the vulnerability on the server side and thus obtain access to the machine.
In fact, security researchers at Trustwave created proof-of-concept code that would cause the buffer overflow using the pingback feature in WordPress.
Multiple Linux distributions are affected
Ghost is present in glibc versions up to 2.17, which was made available in May 21, 2013. The latest version of glibc is 2.20, available since September 2014.
However, at that time it was not promoted as a security fix and was not included in many Linux distributions, those offering long-term support (LTS) in particular.
Among the impacted operating systems are Debian 7 (wheezy), Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and 7, CentOS 6 and 7, Ubuntu 12.04. Luckily, Linux vendors have started to distribute updates with the fix that mitigates the risk. Users are advised to waste no time downloading and applying them.
In order to demonstrate the flaw, Qualys has created an exploit that allowed them remote code execution through the Exim email server. The security company said that it would not release the exploit until the glitch reached its half-life, meaning that the number of the affected systems has been reduced by 50%.
Vulnerable application in Linux are clockdiff, ping and arping (under certain conditions), procmail, pppd, and Exim mail server.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //