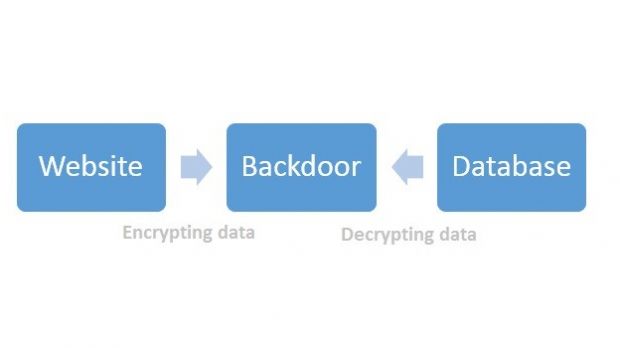
Cybercriminals have expanded their ransomware attacks to entities that are more likely to pay the money and have started to target companies by encrypting important databases used by their websites.
The new scheme requires patience and works by gaining access to the server and encrypting critical fields in a database. When the cybercriminals deem that sufficient time has passed so that all backups of the database contain the encrypted version, they send a ransom request to the victim.
Information is decrypted on the fly, until the key is removed
Security researchers at High-Tech Bridge encountered the new approach, which they dubbed RansomWeb, when investigating an issue with the website of a financial company being out of service on account of a database error.
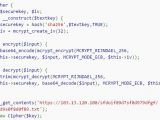
It seems that at fault was a web application that had been compromised six months earlier and some server scripts had been modified to encrypt all content before being added to the database and decrypt it when data was requested.
This method allowed the website to function properly without raising any suspicions, since there was no indication of an attack.
According to the researchers, the encryption key that unlocked the data during the six-month period was stored on a remote server and it would be sent via a secure connection in order to avoid its interception.
“During six months, hackers were silently waiting, while backups were being overwritten by the recent versions of the database. At the day X, hackers removed the key from the remote server. Database became unusable, website went out of service, and hackers demanded a ransom for the encryption key,” High-Tech Bridge writes.
More incidents of this kind are expected to occur
Initially, the security experts believed that the financial institution was the victim of a targeted attack, but a similar case became known to them a week ago. The most recent incident ended with the impossibility of authenticating to a phpBB forum.
Just like in the previous event, the data would be encrypted on the fly between the web application and the database.
Upon analysis, the researchers also discovered two backdoor installation scripts the intruders had left on the server. One of the installers would modify the “config.php” file to include the encryption/decryption routines; the other parsed the available credentials in order to encrypt them.
After two months of waiting, the attackers removed the key from the remote server and delivered their financial demands in its exchange.
“RansomWeb attacks may cause unrepairable damage, they are very easy to cause and pretty difficult to prevent. Days when hackers were attacking websites for glory or fun are over, now financial profit drives them. The era of web blackmailing, racket and chantage is about to start,” said Ilia Kolochenko, CEO of High-Tech Bridge.
He may be right, since vulnerabilities leading to compromising web servers are reported quite often, web applications being the culprit in most of the cases.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //