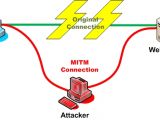
A new type of man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack, called “DoubleDirect” is currently used in the wild to redirect mobile connections to major websites such as Google, Facebook and Twitter to a device controlled by the attacker.
By getting the traffic from the victim, cybercriminals could steal log-in credentials as well as send malware to the targeted mobile device.
Windows and Linux are not affected
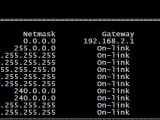
The new method, discovered by researchers at mobile security firm Zimperium, relies on ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) redirect packets to change the routing tables of a host; these are used by routers to announce a machine of a better route for a certain destination.
“However, an attacker can also use ICMP Redirect packets to alter the routing tables on the victim host, causing the traffic to flow via an arbitrary network path for a particular IP. As a result, the attacker can launch a MITM attack, redirecting the victim’s traffic to his device,” say Zimperium researchers in a blog post explaining the method.
According to the company, the devices running iOS (including 8.1.1), Android (including Lollipop) and OS X (including Yosemite) accept ICMP redirect packets by default and, as such, are the most vulnerable to the attack. This does not happen in the case of Windows and Linux, though, because these operating systems do not accept ICMP redirect packets.
Regularly, ICMP Redirect attacks are known to be half-duplex MitM, which means that the node is limited to either receiving or transmitting information (it cannot do both at the same time). With the DoubleDirect attack, cybercriminals achieved full-duplex MitM, as the node can both send and receive data (only one message) at the same time.
Attacks have been spotted in 31 countries
After analyzing the attacks in the wild, Zimperium created a proof-of-concept that demonstrates the possibility of a full-duplex ICMP redirect attack by predicting the IP addresses the victim tries to connect to, by sniffing the DNS traffic of the target; the next step consists of sending an ICMP redirect packet to all IP addresses.
Zimperium says that attacks have been observed in 31 countries, including Australia, Israel, Finland, United Kingdom, Austria, Canada, Brazil, Russia, United States, China, Italy, France and Germany.
Apart from traffic to Google, Facebook and Twitter, the company noticed other destinations, such as Hotmail, Live.com, Naver.com.
Researchers say that using the DoubleDirect method attackers could compromise a mobile device as well as a corporate network.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //