Researchers have found that a localized version of TorLocker, a piece of crypto-malware related to CryptoLocker, is distributed to Japanese speakers as part of an affiliate program operated by cybercriminals.
As soon as the malware is launched on the system, it proceeds to encrypt files with certain extensions, holding them in a locked state until a ransom is paid by the victim in exchange for decrypting them.
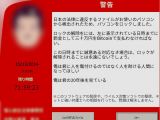
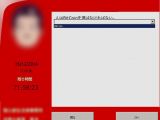
The fee demanded by the cybercriminals is displayed in a ransom message that appears after the targeted data has been processed and ranges between $500 / €400 and $3,600 / €2,900.
TorLocker is part of a larger operation
Symantec confirms that there are multiple variants of this particular threat currently targeting Japanese speakers.
The company explains in a blog post that the malware is part of a grander scheme that offers cybercriminals the possibility to create a custom ransomware based on a malware building toolkit.
Additional options available in the program include access to the control panel of TorLocker, which provides information about the number of infections. In exchange, the crooks renting the infrastructure have to share a percentage of the profit with the operators of the program.
The researchers say that the Japanese variants of the ransomware are distributed through compromised websites, most of them hosting blogs.
“However, it is also possible that the attacker is renting an exploit kit [RIG EK] to automatically compromise victims’ computers by exploiting software vulnerabilities,” the security experts say.
Users tricked with Flash Player installation page
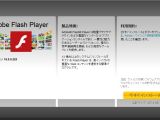
In one case, they observed TorLocker being distributed from a compromised website that showed a fake download page for Adobe Flash Player.
Users falling for the trick would be served an unsigned file that did not even sport the Flash icon typical for the Adobe program. These would be clear indicators that the executable is not what it pretends to be.
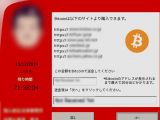
After the encryption process completes, the victim is shown the ransom message in Japanese, asking for payment in bitcoin digital currency.
Security experts recommend victims not to comply with the extortion demands because the attackers may not offer the means to decrypt the files once they receive the money. Another reason is to discourage this type of criminal activity; if money is not paid, there is no use for crooks to engage in campaigns of this sort.
The best form of protection against such threats is to create a backup system, at least for the most important data. In case of compromise, the files can be restored after the computer has been properly cleaned.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //